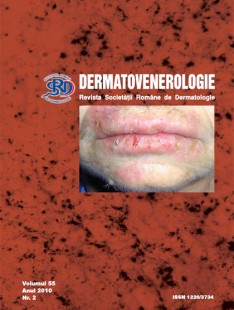
Clinical cases
Treatment with rituximab in epidermolysis bullosa acquisita: clinical response, effect on B-cell activating factor
The B-cell activating factor (BAFF), a member of the TNF family, regulates the survival and proliferation of B cells. Here we investigated clinical response, changes in BAFF levels and titers of circulating antibodies in a Rituximab-treated case of severe epidermolysis bullosa acquisita (EBA) within 1 year.
The diagnosis of EBA was confirmed with routine histology, direct immunofluorescence, indirect immunofluorescence using salt-split skin and immunoblotting. After the 4 weekly infusion of Rituximab (375 mg/m2) the patient had a partial remission of the skin and mucous membrane lesions.
The clinical response was accompanied by a strong elevation of circulating levels of BAFF and an important reduction in serum IgG autoantibodies. The increase in BAFF levels after Rituximab therapy could have promoting effects on antibody production by long-lived antigen-specific plasma cells. Therefore, a BAFF-antagonist treatment could be considered to prolong the period of clinical remission.